flightlog2x#
Overview#
A suite of tools to generate beautifully annotated KML/KMZ files (and other data) from inav blackbox logs, OpenTX log files (inav S.Port telemetry, some support for OpenTX logs from Ardupilot), BulletGCSS and Aurduplot .bin logs.
- flightlog2kml - Generates KML/Z file(s) from Blackbox log(s), OpenTX (OTX) and Bullet GCSS logs (with optional mission file and CLI file for display of
mission/fwapproach/safehome/geozone). - fl2mqtt - Generates MQTT data to stimulate the on-line Ground Control Station BulletGCSS
- fl2ltm - If
fl2mqttis installed (typically by hard or soft link) asfl2ltmit generates LTM (inav's Lightweight Telemetry). This is primarily for use by mwp as a unified replay tool for Blackbox, OpenTx, BulletGCSS and Aurduplot.binlogs. - log2mission - Converts a flight log (Blackbox, OpenTx, BulletGCSS, AP) into a valid inav mission. A number of filters may be applied (time, flight mode).
- mission2kml - Generate KML file from inav mission files (and other formats) and CLI files (
safehome,fwapproach,geozone).
flightlog2kml#
$ flightlog2kml --help
Usage of flightlog2kml [options] file...
-attributes string
Attributes to plot (effic,speed,altitude) (default "effic,speed,altitude,battery")
-cli string
Optional CLI file name
-config string
alternate file
-dms
Show positions as DD:MM:SS.s (vice decimal degrees) (default true)
-dump
Dump log headers and exit
-efficiency
Include efficiency layer in KML/Z (default true)
-energy-unit string
Energy unit [mah, wh] (default "mah")
-extrude
Extends track points to ground (default true)
-gradient string
Specific colour gradient [red,rdgn,yor] (default "yor")
-home-alt int
[OTX] home altitude
-index int
Log index
-interval int
Sampling Interval (ms) (default 1000)
-kml
Generate KML (vice default KMZ)
-mission string
Optional mission file name
-mission-index int
Optional mission file index
-outdir string
Output directory for generated KML (default "/tmp")
-rebase string
rebase all positions on lat,lon[,alt]
-rssi
Set RSSI view as default
-split-time int
[OTX] Time(s) determining log split, 0 disables (default 120)
-summary
Just show summary
-version
Just show version
-visibility int
0=folder value,-1=don't set,1=all on
flightlog2kml 1.0.15 commit:2d2446a
Multiple logs (with multiple log indices) may be given. A KML/Z will be generated for each file / index.
The output file is named from the base name of the source log file, appended with the index number and .kml or .kmz as appropriate. For example:
$ flightlog2kml LOG00044.TXT
Log : LOG00044.TXT / 1
Flight : "Model" on 2020-04-12T14:24:01.410+03:00
Firmware : INAV 2.4.0 (bcd4caef9) MATEKF722 of Feb 11 2020 22:48:59
Size : 19.36 MB
Altitude : 292.8 m at 25:42
Speed : 28.0 m/s at 13:54
Range : 17322 m at 14:22
Current : 30.6 A at 00:05
Distance : 48437 m
Duration : 43:44
Disarm : Switch
Output : /tmp/LOG00044.1.kmz
results in the KMZ file /tmp/LOG00044.1.kmz
Where -mission <file> is given, the given waypoint <mission file> will be included in the generated KML/Z; mission files may be one of the following formats as supported by impload:
- MultiWii / XML mission files (MW-XML) mwp, inav-configurator, ezgui, mission planner for inav, drone-helper).
- mwp JSON files
- apmplanner2 "QGC WPL 110" text files
- qgroundcontrol JSON plan files
- GPX and CSV (as described in the impload user guide)
If you use a format other than MW-XML it is recommended that you review any relevant format constraints as described in the impload user guide.
For INAV multi-mission files, -mission-index may be used to define which segment of a multi-mission file to use (1 based).
Output#
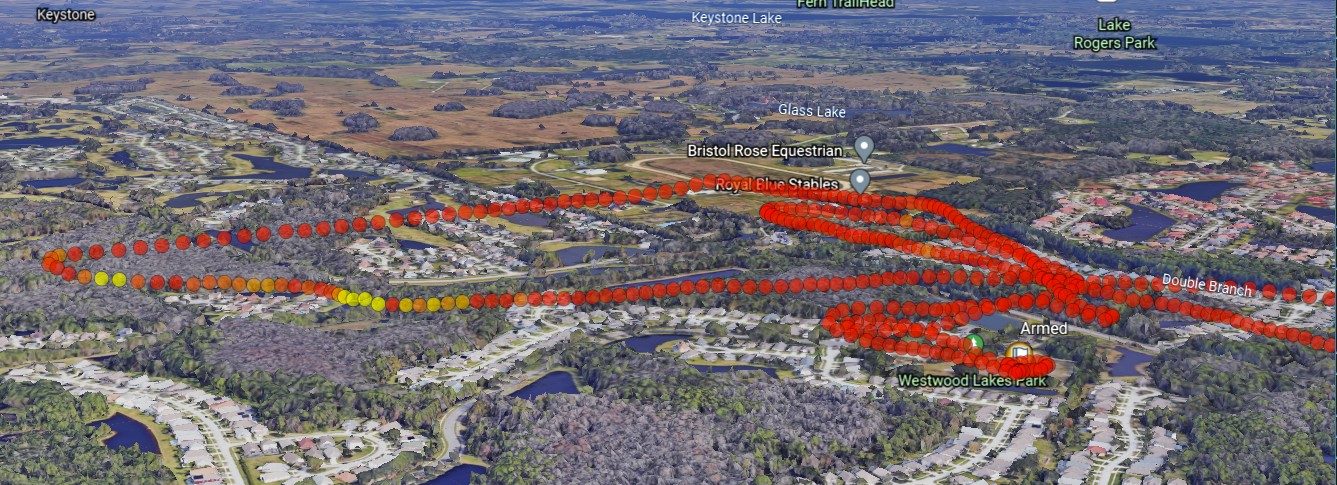
KML/Z file defining tracks which may be displayed Google Earth. Tracks can be animated with the time slider.
Both Flight Mode and RSSI tracks are generated; the default for display is Flight Mode, unless -rssi is specified (and RSSI data is available in the log). The log summary is displayed by double clicking on the file name folder in Google Earth.
Modes#
flightlog2kml can generate three distinct colour-coded outputs:
- Flight mode: the default, colours as below.
- RSSI mode: RSSI percentage as a colour gradient, according to the current
--gradientsetting. Note that if no valid RSSI is found in the log, this mode will be suppressed. - Efficiency mode: The efficiency (mAh/km) as a colour gradient, according to the current
--gradientsetting. This is not enabled by default, and requires the--efficiencysetting to be specified, either as a command line option or permanently in the configuration file.
Flight Mode Track#
- White : WP Mission
- Yellow : RTH
- Green : Pos Hold
- Lighter Green : Alt Hold
- Purple : Cruise
- Cyan : Piloted
- Lighter cyan : Launch
- Red : Failsafe
- Orange : Emergency Landing
Colour Gradients#
The RSSI and Efficiency modes are displayed using a colour gradient. Three gradients are available:
- red : The default, white representing the best (100%), red the worst (0%)
- rdgn : Red to green, green representing the best (100%), red the worst (0%)
- yor : Yellow/Orange/Red, yellow representing the best (100%), red the worst (0%)
If no option is given, red is assumed. Values are set by the --gradient command line option or in the configuration file.
Examples#
Note: These images are rather old, it looks rather better now.
Flight Modes#
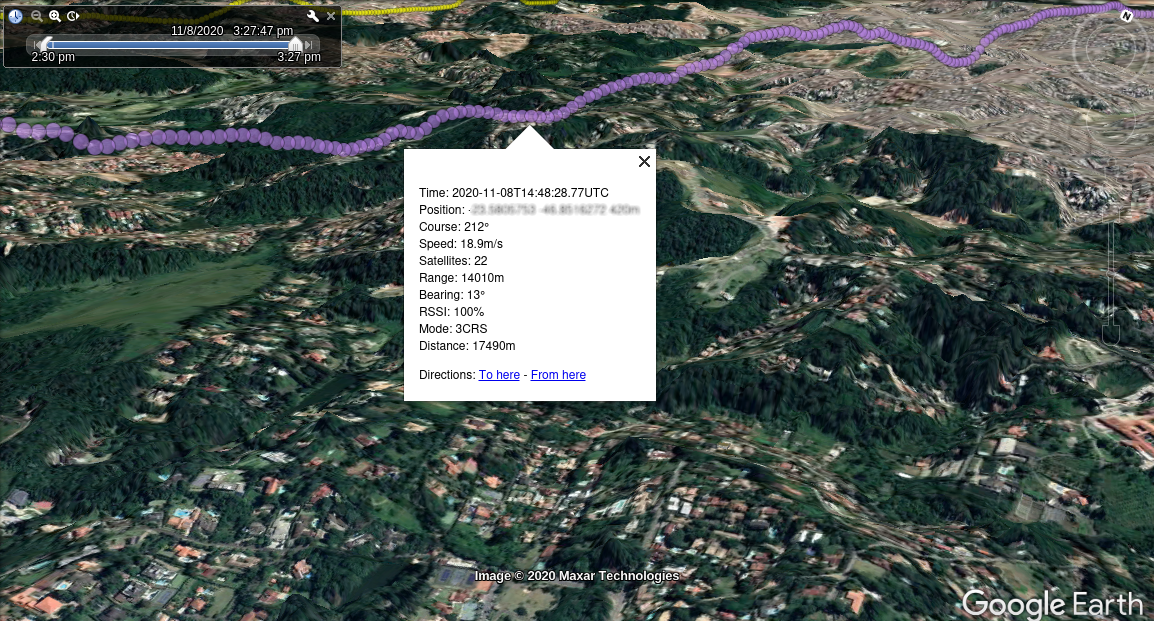
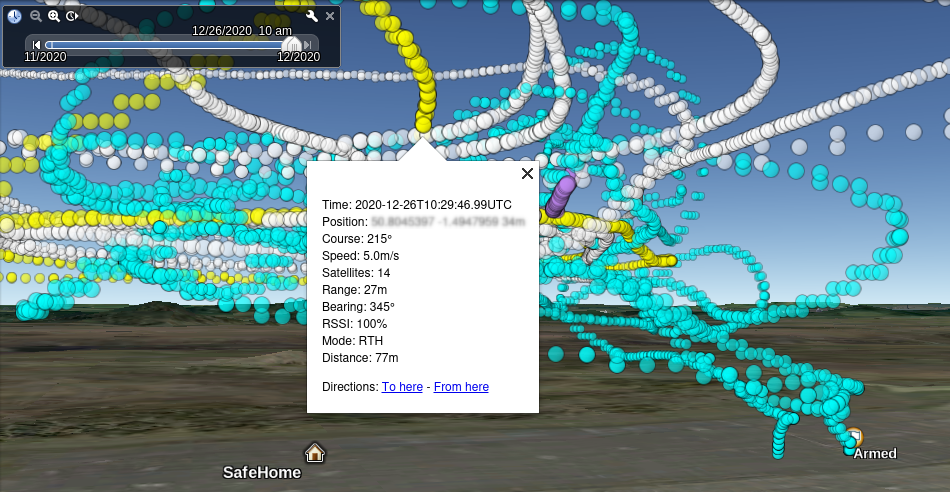
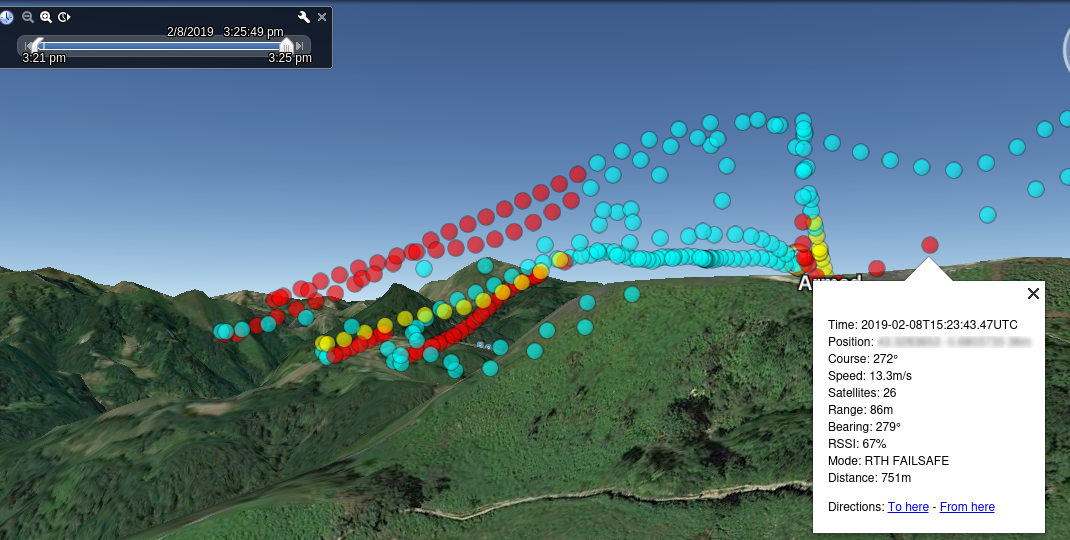
RSSI#
Mission and CLI#
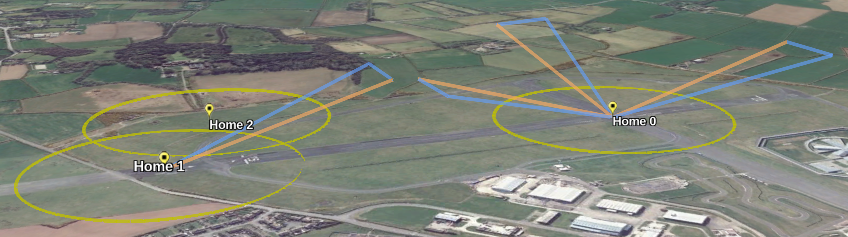
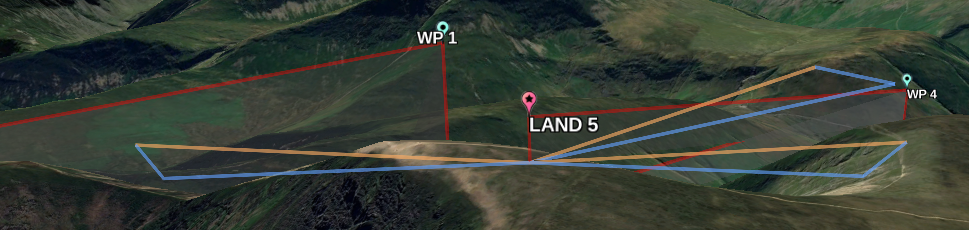
Using OpenTX logs#
There are a few issues with OpenTX logs, the first of which needs OpenTX 2.3.11 (released 2021-01-08) to be resolved:
- CRSF logs in OpenTX 2.3.10 do not record the FM (Flight Mode) field. This makes it impossible to determine flight mode, or even if the craft is armed. Currently
flightlog2kmltries to evince the armed state from other data. - GPS Elevation. Unless you have a GPS attached to the TX, you don't get GPS altitude. This can be set by the
-home-alt Hvalue (in metres). Otherwiseflightlog2kmlwill use an online elevation service. - OpenTX creates a log per calendar day (IIRC), this means there may be multiple logs in the same file. Delimiting these individual logs is less than trivial, to some degree due to the prior CRSF issue which means arm / disarm is not reliably available. Currently,
flightlog2kmlassumes that a gap of more than 120 seconds indicates a new flight. The-split-timevalue allows a user-defined split time (seconds). Setting this to zero disables the log splitting function.
fl2mqtt#
The MQTT option (for BulletGCSS) uses a MQTT broker URI, which may include a username/password and cafile if required for authentication and/or encryption. It can also generate compatible log files that may be replayed by BulletGCSS' internal log player (without requiring a MQTT broker).
$ fl2mqtt --help
Usage of fl2mqtt [options] file...
-blt-vers int
[MQTT] BulletGCSS version (default 2)
-broker string
Mqtt URI (mqtt://[user[:pass]@]broker[:port]/topic[?cafile=file]
-dump
Dump log headers and exit
-home-alt int
[OTX] home altitude
-index int
Log index
-interval int
Sampling Interval (ms) (default 1000)
-logfile string
Log file for browser replay
-mission string
Optional mission file name
-rebase string
rebase all positions on lat,lon[,alt]
-split-time int
[OTX] Time(s) determining log split, 0 disables (default 120)
The BulletGCSS wiki describes how the broker values are chosen; in general:
- It is safe to use
broker.emqx.ioas the MQTT broker, this is default if no broker host is defined in the URI. - You should use a unique topic for publishing your own data, this is slash separated string, for example
foo/bar/quux/demo; the topic should include at least three elements. - If you want to use a TLS (encrypted) connection to the broker, you may need to supply the broker's CA CRT (PEM) file. A reputable test broker will provide this via their web site.
Note that the scheme (mqtt:// in the --help text) is interpreted as:
- ws - Websocket (vice TCP socket), ensure the websocket port is also specified
- wss - Encrypted websocket, ensure the TLS websocket port is also specified. TLS validation is performed using the operating system.
- mqtts,ssl - Secure (TLS) TCP connection. Ensure the TLS port is specified. TLS validation is performed using the operating system, unless
?cafile=fileis specified. - mqtt (or any-other scheme) - TCP connection. If
?cafile=fileis specified, then that is used for TLS validation (and the TLS port should be specified).
There is a bb2kml wiki article describing how to host your own MQTT broker, for reasons of convenience or better privacy.
Example:
## the default broker is used ##
$ fl2mqtt -broker mqtt://broker.emqx.io/org/mwptools/mqtt/playotx openTXlog.csv
$ fl2mqtt -broker mqtt:///org/mwptools/mqtt/playbbl blackbox.TXT
## broker is test.mosquitto.org, over TLS, needs cafile with self-signed certificate
## note the TLS port is also given (8883 in this case)
$ fl2mqtt -broker mqtt://test.mosquitto.org:8883/fl2mqtt/fl2mtqq/test?cafile=mosquitto.org.crt -mission simple_jump.mission BBL_102629.TXT
## No cafile needed, validated certificate
$ fl2mqtt -broker mqtts://broker.emqx.io:8883/fl2mqtt/fl2mtqq/test -mission simple_jump.mission BBL_102629.TXT
## Web sockets (plain text / TLS); mosquitto:8081 has valid Lets Encrypt cert.
$ fl2mqtt -broker ws://test.mosquitto.org:8080/fl2mqtt/fl2mtqq/test -mission simple_jump.mission BBL_102629.TXT
$ fl2mqtt -broker wss://test.mosquitto.org:8081/fl2mqtt/fl2mtqq/test -mission simple_jump.mission BBL_102629.TXT
If a mission file is given, this will also be displayed by BulletGCSS, albeit incorrectly if there WP contains types other than WAYPOINT and RTH.
mwp can also process / display the BulletGCSS MQTT protocol, using a similar URI definition.
log2mission#
log2mission will create an inav XML mission file from a supported flight log (Blackbox, OpenTX, BulletGCSS). The mission will not exceed the inav maximum of 120 mission points (or configurated maximum).
From log2mission 1.0.17 and Blackbox logs from INAV 7.1.0 and later, the active waypoint number is stored in the log and the majority of filtering options are ignored.
For such logs (log2mission 1.0.17+, INAV BBL 7.1.0+):
-start-offset,-end-offset,-epsilon,-max-wp,-mode-filter,-split-timehave no effect and are ignored.- You should probably use a lower
-interval(for example 10).
Usage#
$ log2mission
Usage of log2mission [options] file...
-end-offset int
End Offset (seconds) (default -30)
-epsilon float
Epsilon (default 0.015)
-index int
Log index
-interval int
Sampling Interval (ms) (default 1000)
-max-wp int
Maximum WPs in mission (default 120)
-mode-filter string
Mode filter (cruise,wp)
-rebase string
rebase all positions on lat,lon[,alt]
-split-time int
[OTX] Time(s) determining log split, 0 disables (default 120)
-start-offset int
Start Offset (seconds) (default 30)
log2mission 0.12.3, commit: 43e033d
- The
start-offsetandend-offsetcompensate for the fact that the start / end of the flight is usually on the ground, and thus is not a good WP choice. The defaults are 30 seconds for the start offset and -30 seconds (i.e. 30 seconds from the end) for the end offset. The end offset may be specified as either a positive number of seconds from the start of the log or a negative number (from the end). Locations prior to the start offset and after the end offset are not considered for mission generation. If theend-offsetis specified (0 cancels it), and there is no flight mode filter, then RTH is included in the generated mission. - The
mode-filterallows the log to filtered on Cruise and WP modes, e.g.-mode-filter=cruise,-mode-filter=wp,-mode-filter=cruise,wp. Ifmode-filteris specified, log entries not in the required flight mode(s) are discarded. Cruise includes both 2D and 3D cruise.
epsilon tuning#
The epsilon value is an opaque factor that controls the point simplification process (using the Ramer–Douglas–Peucker algorithm). The default value should be a good starting point for fixed wing with reasonably sedate flying. On a multi-rotor in a small flight area, a much smaller value (e.g. 0.001) would be more appropriate. Increasing the value will decrease the number of mission points generated. log2mission will do this automatically if the default value results in greater than max-wp mission points, for example: the log below would generate more than 70 points with the default epsilon value; too many if we are targeting inav 3.0.2 or earlier .
$ log2mission -start-offset 60 -end-offset -120 -max-wp 60 /t/inav-contrib/otxlogs/demolog.TXT
Flight : MrPlane on 2021-04-08 13:24:07
Firmware : INAV 3.0.0 (fc0e5e274) MATEKF405 of Apr 7 2021 / 17:02:08
Size : 19.36 MB
Log : demolog.TXT / 1
Speed : 28.0 m/s at 13:54
Range : 17322 m at 14:22
Current : 30.6 A at 00:05
Distance : 48437 m
Duration : 43:44
Altitude : 292.8 m at 25:42
Mission : 56 points (reprocess: 1, epsilon: 0.018)
The output from this example would be demolog.1.mission
multirotor example#
With the default epsilon of 0.015, for a "small field" MR flight, it is often the case that no useful mission would be generated from a such "short/complex" flight, prior to the 0.98 release auto-correction, for example:
$ log2mission logfs.TXT
...
Mission : 2 points
For 0.9.8 and later, log2mission will make an attempt to resolve the "short/complex" 2 point results by increasing epsilon automatically.
$ log2mission /t/inav-contrib/logfs.TXT
Log : logfs.TXT / 1
...
Mission : 14 points (reprocess: 1, epsilon: 0.001000)
Some experimentation may still be required to get a good mission, particularly for shorter MR flights. In particular, if reprocessing is indicated and the number of generated points is close to max-wp, then it's probably worth running again with a slightly larger epsilon than that shown in the output. Likewise, where log2mission has decreased the epsilon, it's probably worth running log2mission again with a slightly smaller epsilon than indicated.
mission2kml#
A standalone mission file to KML/Z converter is also provided.
$ mission2kml --help
Usage of mission2kml [options] files...
-dms
Show positions as DMS (vice decimal degrees)
-home string
Use home location
-mission-index int
Mission Index
-out string
Output file (default "-")
The home location is given as decimal degrees latitude and
longitude and optional altitude. The values should be separated by a single
separator, one of "/:; ,". If space is used, then the values must be enclosed
in quotes.
In locales where comma is used as decimal "point", then comma should not be
used as a separator.
If a syntactically valid home position is given, without altitude, an online
elevation service is used to adjust mission elevations in the KML.
Examples:
-home 54.353974/-4.5236
--home 48,9975:2,5789/104
-home 54.353974;-4.5236
--home "48,9975 2,5789"
-home 54.353974,-4.5236,24
A KML file is generated to stdout or the file given with -out.
$ mission2kml -out mtest.kml -home 54.125229,-4.730443 barrule-h.mission
Note that for recent MW-XML mission files generated by mwp or the INAV-configurator, the planned home located may be saved in the mission files; in which case it will be used.
An optional CLI file will be parsed for safehome and fwapproach and geozone information. It is not necessary to specify a mission file in order to visualise CLI defined elements.
# combined.txt is a CLI diff with safehome, fwapproach and geozone lines
# No mission file is requried
$ mission2kml -out /tmp/ll.kml combined.txt
Setting default options#
Default settings may be set in a JSON formatted configuration file.
- On POSIX platforms (Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS),
$HOME/.config/fl2x/config.json - On Windows
%LOCALAPPDATA%\fl2x\config.json
The keys in the file are the relevant command line options, the following are recognised:
attributesdmsextrudekmlrssiefficiencysplit-timehome-altblackbox-decodegradientoutdirblt-verstypevisibilityenergy-unitmax-wpfast-is-redlow-is-red
For example, the author's config.json:
{
"dms" : true,
"extrude" : true,
"gradient" : "yor",
"attributes" : "effic,speed,altitude,battery",
"rssi" : false,
"efficiency" : true,
"outdir" : "/tmp",
"kml" : false,
"fast-is-red" : true,
"low-is-red" : true
}
A warning will be displayed if the configuration file in not syntactically correct; in such cases its contents will be ignored. There is a somewhat complete example in the wiki that can be used as a template.
JSON Syntax
The keys in the JSON file use hyphen (-), not underscore (_).
Note also that the command interpreter allows -flag or --flag for any option.
Limitations, Bugs, Bug Reporting#
flightlog2kml aims to support as wide a range of inav firmware and log decoders as possible. During its development, inav has changed both the data logged and in some cases, the meaning of logged items; thus for versions of inav prior to 2.0, the reported flight mode might not be completely accurate. flightlog2kml is known to work with logs from 2015-10-30 (i.e. pre inav 1.0), and if you have a Blackbox log that is not decoded / visualised correctly, please raise a Github issue; this is a bug.
Due to the range of inav versions, blackbox_decode versions and supported operating systems, when reporting bugs, please include the following information in the Github issue:
- The version of
flightlog2kmlandblackbox_decode. Both applications have a--helpoption that should give the version numbers. - The host operating system and version (e.g. "Debian Sid", "Windows 10", "MacOS 10.15").
- Provide the blackbox log that illustrates the problem. If you don't want to post the log into an essentially public forum (the Github issue), then please propose a private delivery channel.
Replaying Ardupilot logs requires mavlogdump.py.
Build and Install#
Release media#
Binaries are provided for common operating systems in the Release folder.
Install from release archive#
For example (adjust version number, OS, archiver as necessary).
$ wget https://github.com/stronnag/bbl2kml/releases/download/0.12.0/flightlog2kml-0.12.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
$ tar -xvf flightlog2kml-0.12.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
fl2x/linux-x86_64/
fl2x/linux-x86_64/bin/
fl2x/linux-x86_64/bin/flightlog2kml
fl2x/linux-x86_64/bin/fl2mqtt
fl2x/linux-x86_64/bin/log2mission
fl2x/linux-x86_64/bin/mission2kml
fl2x/linux-x86_64/bin/fl2ltm
fl2x/linux-x86_64/bin/bbsummary
# install locally
$ cp -a fl2x/linux-x86_64/bin/* ~/.local/bin/
# Or system wide
$ sudo cp -a fl2x/linux-x86_64/bin/* /usr/local/bin/
The fl2x tools require that inav blackbox_decode is installed and can be found by the operating system (e.g. $PATH / %PATH%).
On Windows, as long as inav blackbox_decode can be found (which may mean on %PATH% or in the same directory as flightlog2kml (and the other tools), then dropping logs onto flightlog2kml is supported.
Setting the Windows path#
In order to have a simple setup on Windows / drag and drop for both blackbox_decode and flightlog2kml, one strategy might be to have the required applications in a single directory.
Building from source#
Requires Go v1.13 or later. Compiled with:
$ go build cmd/flightlog2kml/main.go
$ go build cmd/mission2kml/main.go
or more simply
# First time
meson build --prefix=~/.local
cd build
ninja install
# Subsequently
cd build
ninja install
flightlog2kml depends on twpayne/go-kml, an outstanding open source Golang KML library.
flightlog2kml may be built for all OS for which a suitable Golang is available. At runtime, it also requires inav's blackbox_decode; the latest version is recommended; the minimum blackbox_decode version is 0.4.4.
For Windows' users it is probably easiest to copy inav's blackbox_decode.exe into the same directory as flightlog2kml.exe, or use the fl2xui GUI application.
Notes
fl2ltmis a link tofl2mqttbbsummaryis a link toflightlog2kmland will behave asflightlog2kml -summary.fl2ltmwill be automatically detected by mwp and used in preference to its olderreplay_bbox_ltm.rbandotxloghelpers.
Graphical User Interface#
There is a graphical user interface for flightlog2kml. Binaries are provided for Linux (.deb).